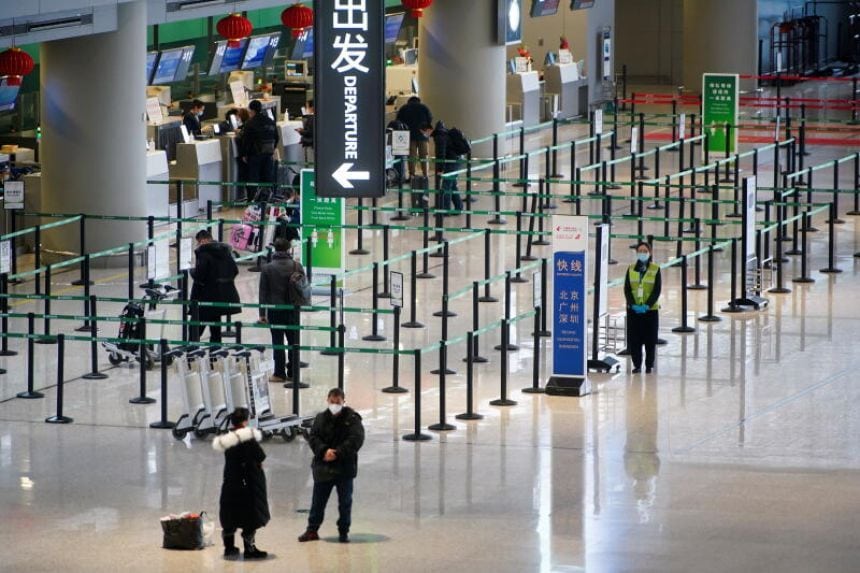
World’s First: China Takes the Lead on “Vaccine Passport”
2021-03-10
Things to note for Singapore VCC taxation
2021-04-15
Variable Capital Companies (VCC) in Singapore
About Variable Capital Companies (VCC)

Image source:ACRA
The Variable Capital Company (VCC) is a new corporate structure for investment funds constituted under the Variable Capital Companies Act which took effect on 14 Jan 2020. The VCC will complement the existing suite of investment fund structures available in Singapore.
Some key features of a VCC
- A VCC has a variable capital structure that provides flexibility in the issuance and redemption of its shares. It can also pay dividends out of capital, which gives fund managers flexibility to meet dividend payment obligations.
- A VCC can be set up as a single standalone fund or an umbrella fund with two or more sub-funds, each holding a portfolio of segregated assets and liabilities.
- A VCC can be used for both open-ended and closed-end fund strategies.
- Fund managers may incorporate new VCCs or re-domicile their existing overseas investment funds with comparable structures by transferring their registration to Singapore as VCCs.
- VCCs must maintain a register of shareholders, which need not be made public. However, this register must be disclosed to public authorities upon request for regulatory, supervisory and law enforcement purposes.
- Assets and liabilities of each sub-fund are to be segregated such that the assets of one sub-fund cannot be used to discharge the liabilities of another sub-fund.
- For common assets and liabilities, including shared costs incurred by umbrella VCCs for the sub funds, the VCC manager needs to establish a fair method of allocation between the sub-funds.

Accounting Implication of a VCC
- An umbrella VCC must maintain separate records and financial statements for each sub-fund. Each VCC must have audited financial statements for each financial year/period which gives true and fair view of the financial performance of the standalone CC or in the case of an umbrella VCC, for each sub-fund.
- VCCs have the flexibility to use not just Singapore Financial Reporting Standards but also International Financial Reporting Standards and US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. Consistent with the sole object of a VCC and the implied constitution of every VCC, we expect that a VCC should meet the criteria to be considered as an investment entity in accordance with IFRS 10, and apply the exception to consolidation. I
- Investments of a VCC, including those through a subsidiary investment vehicles (if any), are measured at fair value through profit or loss in accordance with IFRS 9. In accordance to IFRS 13, fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
- The constitution of the VCC provides flexibility for distribution and reduction of capital as and when determined by the manager. As shares of the VCC are to be issued, redeemed or repurchased at a price equal to the proportion of the net asset value of the VCC represented by each share, there needs to be reliable systems and processes in place to calculate the net asset value of the VCC as and when shares are issued, redeemed or repurchased (daily, monthly or quarterly, as prescribed by the constitution). This may pose challenges to private equity and venture capital funds in particular as up-to-date fair value information may not be readily available to facilitate the calculation of net asset value during a share issuance, redemption or repurchase.
For more information about VCC, please contact us and we will be happy to help you!